
Office No B-301, Gera Imperium Morwadi Chowk Pimpri pune
+91 9766692824
info@metallixengineering.com

Heat Exchanger
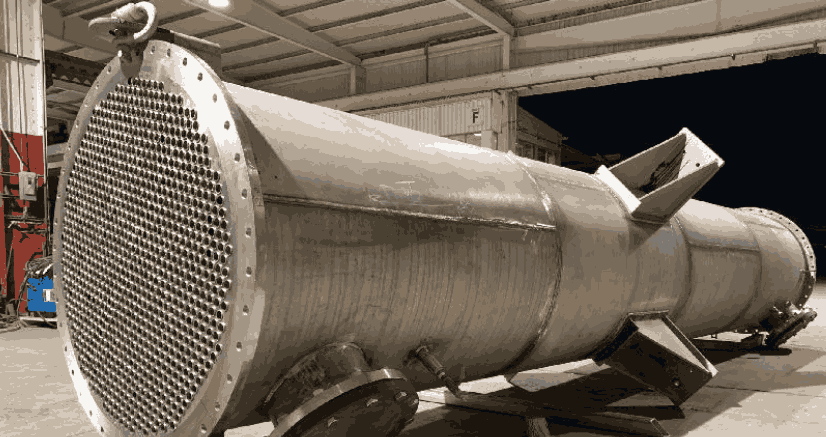
Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a device designed to efficiently transfer heat between two or more fluids—such as liquids, gases, or a combination thereof—without allowing them to mix. This process is fundamental in various industrial and domestic applications, enabling the heating or cooling of fluids to achieve desired temperatures.
Applications of Heat Exchangers
- Power Generation – Employed in boilers, condensers, and cooling systems to manage heat cycles efficiently.
- Oil and Gas Industry – Used in refineries for processes like distillation and cracking, where precise temperature control is essential.
- HVAC Systems – Central to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, ensuring optimal indoor climate control.
- Automotive Industry – Radiators act as heat exchangers, dissipating engine heat to prevent overheating.
Flow Arrangements in Heat Exchangers
Parallel Flow
Both fluids enter the exchanger at the same end and move parallel to each other.
Counterflow
Fluids enter from opposite ends, flowing in opposite directions. This arrangement is often more efficient,
Crossflow
Fluids move perpendicular to each other, commonly used in applications like radiators and air conditioning systems.
Different Types of Heat Exchangers
Shell and Tube Heat
Plate Heat Exchangers
Air-Cooled Heat
Oil Cooler
Kettle Type Heat
U-Tube Heat Exchangers
Services Category
Get in Touch with Us
Our Company Info
Our Services
Quick Link
©2025 Metallix Engineering | All Rights Reserved | Created & Crafted By Itorix Infotech
